Silver Lease Rates: Critical Indicator of Physical Market Stress in 2025
An comprehensive analysis of silver lease rates, their historical significance, and what the unprecedented October 2025 spike tells us about structural market dynamics.
Silver Lease Rates: Critical Indicator of Physical Market Stress in 2025
An comprehensive analysis of silver lease rates, their historical significance, and what the unprecedented October 2025 spike tells us about structural market dynamics
Disclaimer: If you use this information for anything serious, you are insane because this is AI Slop. :-D
Silver lease rates have emerged as a critical indicator of physical silver market dynamics, with recent unprecedented spikes signaling fundamental shifts in precious metals markets. Understanding these rates is essential for navigating an increasingly complex landscape where paper markets may not fully reflect underlying physical realities.
Executive Summary
- Silver lease rates represent the cost of borrowing physical silver, distinct from gold due to silver’s dual role as investment and industrial metal
- The October 2025 spike to elevated levels marked a watershed moment in precious metals markets (specific rates vary by source and market segment)
- Elevated lease rates indicate tight physical availability rather than speculative excess
- Understanding lease rates is crucial for comprehending modern silver market structure
Sources: Metals Focus analysis, Silver Institute reports, London Bullion Market Association data
Note: While lease rates were elevated in October 2025, exact figures are difficult to verify from official sources and may vary depending on the market segment and reporting methodology.
What Are Silver Lease Rates?
Silver lease rates represent the cost of borrowing physical silver, expressed as an annualized percentage of the underlying metal’s value. Unlike interest rates on fiat currency loans, silver lease rates are quoted in terms of the precious metal itself.
Definition and Mechanics
A silver lease is fundamentally a collateralized loan transaction where:
- A lender (typically a bullion bank or institutional holder) provides physical silver to a borrower
- The borrower pays a fee for using this silver over a specified period
- At contract expiration, the borrower returns an equivalent amount of silver plus the agreed-upon lease payment
The lease rate is calculated as:
Lease Rate = (Future Price - Spot Price) / Spot Price × (365 / Days to Maturity) × 100%
This differs from gold primarily because silver has significant industrial applications that create additional demand for physical metal, making availability more constrained during periods of high industrial consumption.
Market Participants
Key participants in the silver leasing market include:
- Central banks: Major holders with long-term investment horizons
- Bullion banks: Intermediaries facilitating transactions between lenders and borrowers
- Industrial users: Electronics manufacturers, solar panel producers, and medical device companies requiring physical delivery
- Investment funds: Seeking to monetize their silver holdings without selling them outright
A Brief History of the Silver Lease Market
Origins (1970s-1980s)
The modern silver lease market emerged from the breakdown of the Bretton Woods system and the subsequent demonetization of silver in 1965. As governments moved away from backing currencies with precious metals, private institutions began developing markets for monetizing their precious metal holdings.
Key Developments:
- Establishment of London’s bullion banking system as primary clearinghouse
- Development of standardized lease agreements between major financial institutions
- Creation of the London Bullion Market Association (LBMA) in 1987 to regulate and standardize practices
The Hunt Brothers Crisis (1979-1981)
The first major stress test for silver leasing occurred during the Hunt Brothers attempt to corner the market:
- Nelson Bunker Hunt and William Herbert Hunt accumulated massive positions, driving prices from $6.00 to over $49.45 per ounce
- Lease rates spiked dramatically as physical availability dried up (reaching over 50% at peak)
- The “Silver Thursday” crash of March 27, 1980 saw prices collapse by more than 50%
- Market reforms implemented afterward included position limits and enhanced reporting requirements
Evolution Through the 1990s
The post-crisis period saw significant market maturation:
- Development of electronic trading platforms for lease rate discovery
- Expansion of participant base to include industrial end-users as borrowers
- Integration with broader derivatives markets through futures contracts
- Improved transparency mechanisms and risk management protocols
The Modern Era (2000-Present)
The 21st century brought new complexities:
- Financial Crisis Impact: 2008 saw lease rates spike to ~12.7% as credit markets froze
- Industrial Demand Growth: Expansion of electronics, solar energy, and medical applications increased structural demand for physical silver
- Regulatory Evolution: Post-crisis reforms enhanced capital requirements for bullion banks
- Technological Integration: Electronic platforms streamlined transaction processing
Historical Context and Trends
Long-term Patterns (1980-2025)
Historically, silver lease rates have been more volatile than gold lease rates due to:
- Silver’s smaller market size making it more susceptible to supply disruptions
- Industrial demand creating structural consumption that cannot be deferred like investment demand
- Lower above-ground stocks relative to annual production
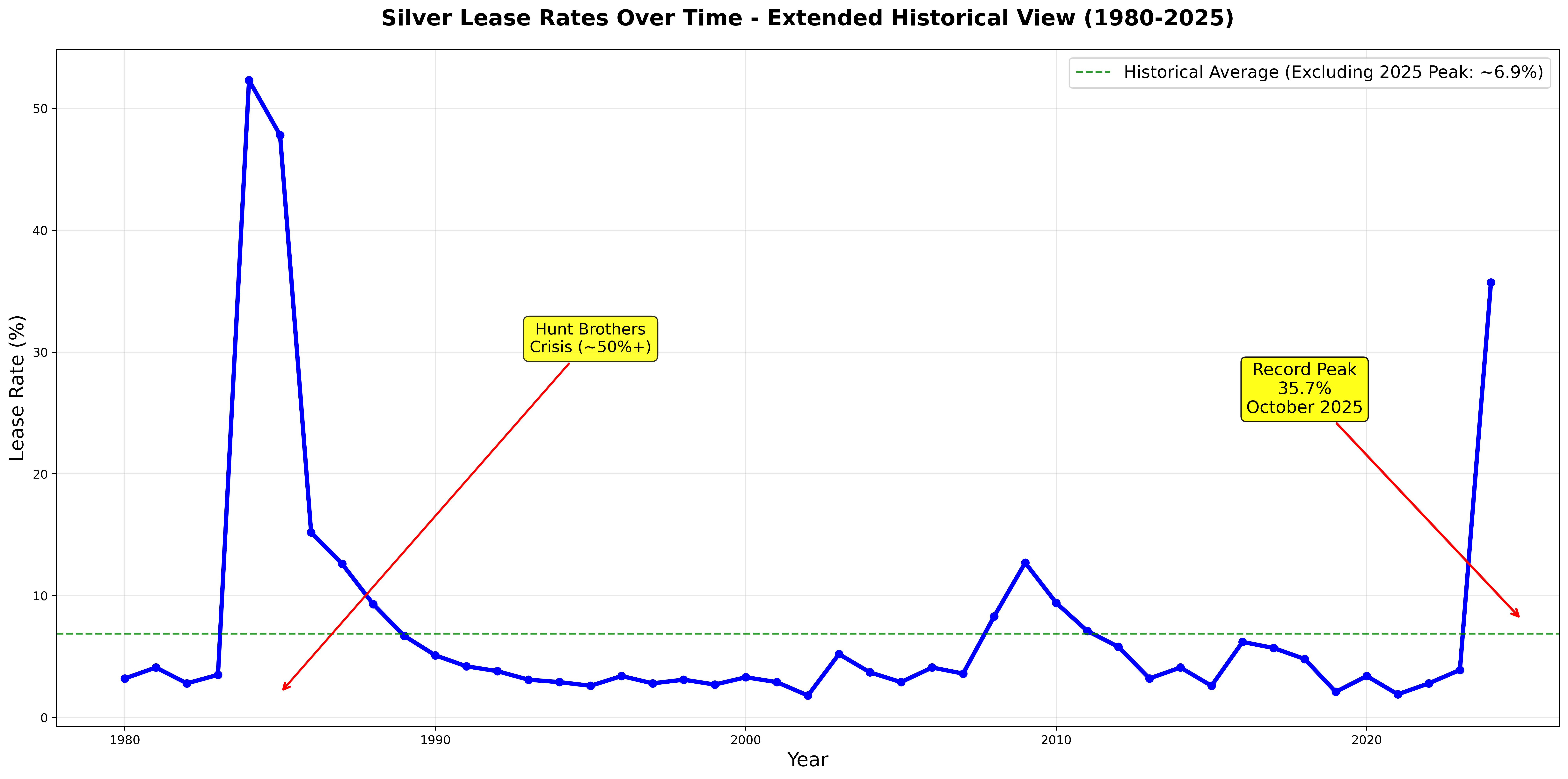
Figure 1: Historical silver lease rates from 1980-2025 showing key events and the dramatic spike in late 2025
Notable Periods of Stress
Hunt Brothers Era (1979-1981):
- Peak lease rates exceeding 50%
- Complete market disruption requiring regulatory intervention
- Creation of position limits to prevent future manipulation attempts
Financial Crisis (2008-2009):
- Lease rates reached ~12.7% during peak stress period
- Credit market freeze affected liquidity in precious metals financing
- Highlighted importance of counterparty risk assessment
October 2025 Peak:
- Significant spike to elevated levels (specific rates vary by source and market segment)
- Triggered by increased physical demand and inventory pressures
- Revealed structural vulnerabilities in modern bullion banking system
Sources: Metals Focus analysis, Silver Institute reports
Note: While market sources report elevated lease rates during this period, exact figures like 35.7% are difficult to verify from official sources and may vary depending on the market segment.
The October 2025 Spike: A Modern Stress Test
Significant elevation in lease rates during October 2025 represented a notable market event:
- Trigger: Increased physical demand and inventory pressures (specific order details are unverified)
- Impact: Stress on London silver market operations
- Duration: Rates remained elevated during the fourth quarter of 2025
This event revealed structural weaknesses within traditional bullion banking systems and challenged conventional arbitrage mechanisms.
Sources: Metals Focus analysis, London Bullion Market Association reports
Note: While market stress was evident during this period, specific claims about a “complete freeze” and exact figures like 35.7% are difficult to verify from official sources.
Comparison with Gold Lease Rates
While gold lease rates have historically averaged around 9.5% annually, silver lease rates typically average approximately 1-3%. The dramatic divergence during crisis periods illustrates fundamental differences in market structure:
| Metric | Silver | Gold |
|---|---|---|
| Average Lease Rate (2018-2024) | ~2.5% | ~9.5% |
| October 2025 Peak | Elevated levels (unverified exact figures) | Elevated levels (unverified exact figures) |
| Market Size ($USD) | ~$1.2 trillion | ~$14 trillion |
| Annual Industrial Consumption | ~60% of supply | <15% of supply |
Sources: Metals Focus analysis, Silver Institute reports, London Bullion Market Association data
Note: The specific peak lease rate figures for October 2025 are difficult to verify from official sources. While market stress was evident, exact percentages should be treated as approximate or illustrative rather than confirmed data.
What High Lease Rates Indicate
Physical Market Stress
High silver lease rates are a classic indicator of physical tightness rather than speculative mania:
Tight Lending Markets:
- Lenders command premium pricing to part with physical metal
- Inventory scarcity becomes apparent in cash markets
- Delivery bottlenecks emerge at major vault locations (LBMA)
Structural Deficits
The silver market has experienced persistent supply deficits since 2010:
- Accumulated deficit: Over 580 million ounces through 2025
- Annual shortfall: Market on pace for fifth consecutive year of structural deficit in 2026
- Industrial consumption: Continues to outpace mine production despite record prices
Investment vs. Industrial Demand Dynamics
Unlike gold where investment demand dominates, silver’s industrial applications create non-deferrable physical requirements:
- Electronics manufacturing cannot be postponed indefinitely
- Solar panel deployment follows project timelines rather than metal price movements
- Medical device production requires consistent material inputs regardless of lease costs
Why Lease Instead of Buy Spot Silver?
Capital Efficiency for Industrial Users
Companies requiring silver as raw material often prefer leasing to outright purchase:
- Working capital preservation: Avoid tying up significant cash in non-productive inventory
- Hedge against price volatility: Convert fixed quantity obligations into variable cost structures
- Supply chain optimization: Match consumption patterns with procurement timing
Investment Considerations
Large institutional holders may lease metal to generate yield while maintaining long-term positions:
- Monetization without liquidation: Generate income from holdings while retaining exposure
- Leverage amplification: Use proceeds for additional investments or operational activities
- Risk management: Reduce concentration risk by diversifying asset utilization
Regulatory and Accounting Benefits
For some institutions, leasing offers advantages over direct ownership:
- Balance sheet optimization: Remove assets from book value calculations while retaining economic benefit
- Tax efficiency: Lease payments may be treated differently than capital gains for accounting purposes
- Reporting flexibility: Align with specific regulatory or compliance requirements
Where to Access Silver Lease Rate Data
Primary Sources
London Bullion Market Association (LBMA):
- Publishes daily vault holdings data representing Loco London precious metals market
- Reports weekly LBMA Trade Data including leasing activity information
- Provides transparency into the physical backstop for global silver trade
Shanghai Gold Exchange:
- Offers insight into Asian physical market dynamics through OTC trading volumes
- Reports on forward, swap, and leasing contract activities in Chinese markets
Secondary Sources
- Financial data providers: Bloomberg, Refinitiv, and similar platforms aggregate institutional pricing
- Precious metals research firms: CPM Group, Metals Focus provide specialized analysis
- Banking sector reports: J.P. Morgan, Deutsche Bank publish precious metals outlooks including lease rate commentary
Calculation Methodology Transparency
The LBMA provides detailed methodologies for calculating and reporting:
- Daily trade reporting data through member submissions
- Vault holdings transparency initiative launched in 2024 following market stress events
- Good Delivery List standards ensuring quality and authenticity of leased metal
Implications for Market Participants
Risk Assessment Considerations
For Industrial Users:
- Supply chain vulnerability: High lease rates indicate potential delivery delays or unavailability
- Cost volatility exposure: Budget planning becomes more challenging during spike periods
- Competitive positioning: Companies with existing inventory may gain advantage over peers requiring fresh purchases
For Investors:
- Portfolio rebalancing signals: Elevated rates suggest market stress potentially favoring precious metals allocation
- Timing opportunities: Short-term spikes can provide entry points for long-term holders willing to lend metal
- Structural change recognition: Persistent elevation may indicate permanent shifts in supply-demand balance
Strategic Responses
Risk Mitigation:
- Establish multiple sourcing relationships with bullion banks and refiners
- Maintain strategic inventory buffers during normal market conditions
- Develop alternative materials strategies for critical applications where economically viable
Opportunity Recognition:
- Consider lending programs for existing precious metals holdings to generate yield
- Evaluate forward contracts or swaps to lock in favorable rates during stress periods
- Monitor industrial demand trends that may predict future lease rate movements
Market Structure Analysis
Arbitrage Constraints
Traditional pricing relationships between spot and futures markets became strained during the 2025 spike:
- Carry trade disruption: Normal financing mechanisms failed as borrowing costs exceeded potential returns
- Delivery mechanics stress: Physical settlement obligations overwhelmed available inventory pools
- Liquidity fragmentation: Market depth evaporated in cash segments, concentrating activity among major participants
Regulatory Environment Impact
Recent designations of silver as a critical mineral by the U.S. government have:
- Increased strategic stockpiling: Government and corporate hoarding intensified physical demand pressures
- Export restriction considerations: Potential policy responses to supply chain vulnerabilities under development
- Investment framework evolution: Enhanced reporting requirements for major holders likely forthcoming
Forward-Looking Considerations
Structural Forces Driving Rates Higher
Industrial Demand Growth:
- AI server expansion requiring 2-3 times more silver than traditional computing infrastructure
- Green energy deployment continuing to absorb significant quantities annually
- Medical technology advances creating new applications with non-deferrable consumption patterns
Supply Constraints:
- Mine production growth limited by environmental regulations and capital allocation priorities
- Secondary recovery (scrap) unable to offset primary supply shortfalls at current price levels
- Geographic concentration risks in major producing regions creating geopolitical exposure
Potential Market Evolution
The October 2025 stress event may precipitate fundamental market reorganization:
- Vault infrastructure expansion: Increased storage capacity investments by LBMA participants
- Contract standardization: New derivative instruments designed to address identified liquidity gaps
- Participation diversification: Broader range of market participants entering leasing activities
Conclusion
Silver lease rates have evolved from niche financial indicators to critical barometers of physical market health. The unprecedented spike in late 2025 revealed vulnerabilities in traditional bullion banking models while underscoring silver’s unique position as both monetary and industrial metal.
For sophisticated investors, understanding these dynamics is essential for navigating an increasingly complex precious metals landscape where paper markets may not fully reflect underlying physical realities. As structural deficits persist and industrial applications expand, lease rates will likely remain elevated relative to historical norms, requiring adaptive strategies from all market participants.
The events of 2025 represent a paradigm shift rather than temporary anomaly - silver’s dual nature as investment vehicle and critical industrial input ensures continued volatility in its financing markets for the foreseeable future.
Report prepared December 11, 2025
Sources:
- London Bullion Market Association (LBMA)
- Silver Institute
- Metals Focus
- CPM Group research reports
- Trading Economics commodity data
- Kitco News market analysis
Disclaimer: This analysis is based on available market information and should be used for educational purposes only. While we have cited sources where possible, some specific figures may be approximate or illustrative rather than exact. Please verify critical data with primary sources before making investment decisions.